ABO Blood Group System & It’s Determination
The Human ‘ABO’ Blood Group System discovered by Landsteiner’s in 1901. The principle of Blood grouping is based on the Landsteiner’s Law.
Landsteiner’s Law :
“The corresponding antibody is never present in the serum of an individual when the antigen is manifest on his red cells”. (Same type of antigen and antibody cannot stay together in an individual).
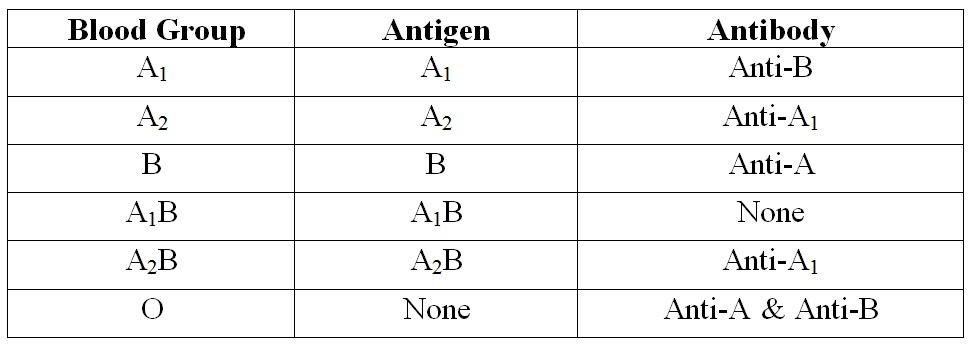
‘ABO’ Blood group system is divided into four major groups and they are ‘A’ group, ‘B’ group, ‘AB’ group and ‘O’ group. This depends on the presence of ‘A’ antigen or/and ‘B’ antigen on the surface of the Red Blood Corpuscles (RBCs) and determined by agglutination reactions obtained by mixing their Red blood cells with two different reagents (corresponding antibodies), known as Anti-A and Anti-B.
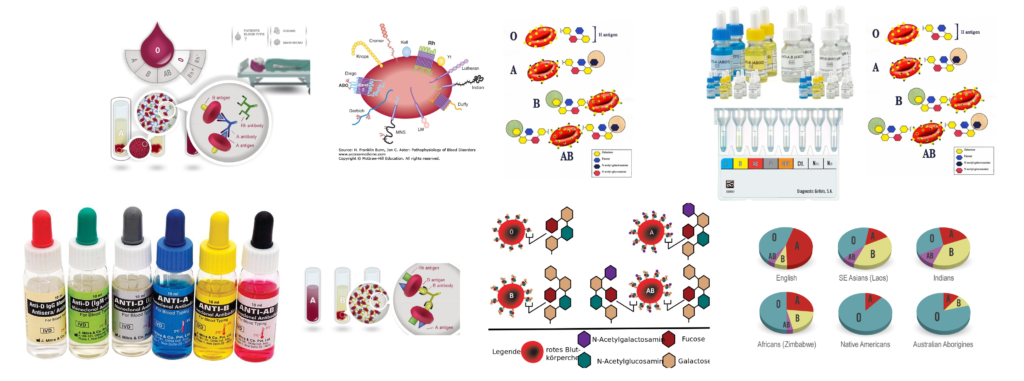
The percentage of different group in Indian and Caucasian (US) population as approximately as follows :
‘ABO’ Group is determined by two methods :
- Forward Grouping
- Reverse Grouping
Subgroup of ‘ABO” Blood Group System
Antigen ‘A’ primarily exists as a strongly reacting A1 antigen while A2 is a weakly reacting antigen found in a few persons. The majority of Group ‘A’ infants appear to belong in subgroup A2 at birth which later become A1.
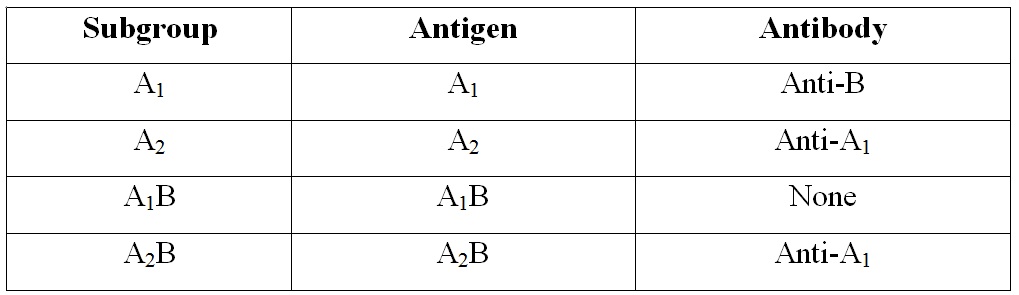
About 20% of Group-A / Group-AB are A2 or A2B; where as 80% is A1 or A1B. The A2 antigen may give only weak reaction with the usual anti-A sera.
A special Agglutinine (Ab) obtained from Seeds (Lectin) with the specificity of anti-A1 will agglutinate all A1 Cells but not A2 Cells. Thus in a Reverse grouping if the serum of an ‘A’ group individual shows the presence of Anti-A; agglutinating A-Cells; the presence of A1 may be suspected. Then treat the ‘A’ Cells of individual with Anti-A1 lectin. If agglutination occurred hence individual’s Blood group A1. If agglutination not occurred then the individual Blood group is A2. Antigen weaker than anti-A are occasionally encountered – called A3, Ax, Ay etc. These variations in ‘A’ antigen of erythrocytes are due to mutant form the Glycosyl Transferases produced by ‘A’ gene. Which are less efficient at transferring N-acetyl-D-galactosamine to H Substance.
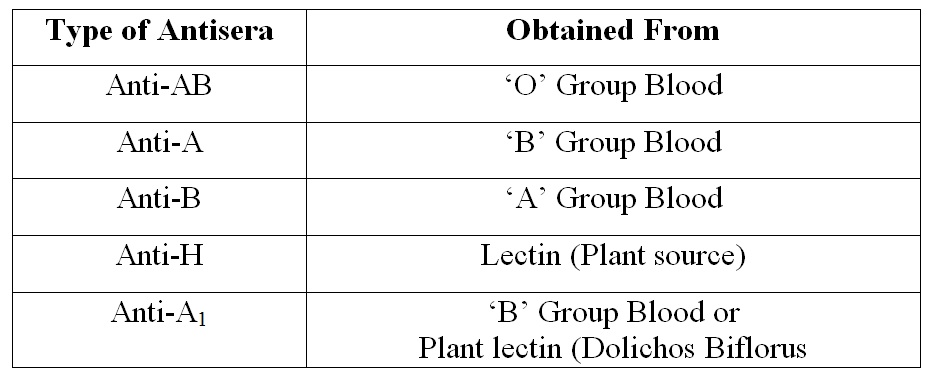
Antisera used in ‘ABO’ test procedure
- Purpose : Forward ‘ABO’ Blood Grouping.
- Type of Antisera and Obtained from :
Criteria of Antisera :
- The titre of Antisera (Anti-A and Anti-B) should be at least 128.
- The Antisera should not haemolysed red blood cells carring the corresponding antigen.
- Every Antisera should be carefully tested for potency, avidity, specificity and freedom from rouleaux formation properties.
Antigen and Antibody present in ‘ABO’ Grouping :

Determination of ‘ABO’ Blood Grouping by Forward Grouping
Determination of blood group by reacting known antibody (anti-A & anti-B) with unknown antigen (present on the surface membrane of the RBCs). It also called Cell Grouping or Direct Grouping.
Principle :
The procedures used with the antisera are based on the principle of agglutination. Normal human red blood cell possessing antigen will clump in the presence of corresponding antibody.
Method :
Three methods are used for determination of ‘ABO’ blood grouping by Forward Grouping technique….
- Slide method
- Tube method
- Gel method
In the developing country Slide method is commonly performed. But Special circumstances Tube method as well as Gel method is performed. In the Laboratory We performed Slide method.
Requirements :
- Clean and dry grass free glass slide.
- Pasteur pipette.
- Applicator sticks.
- Centrifuge machine.
- Timer & Marker pen
- Microscope
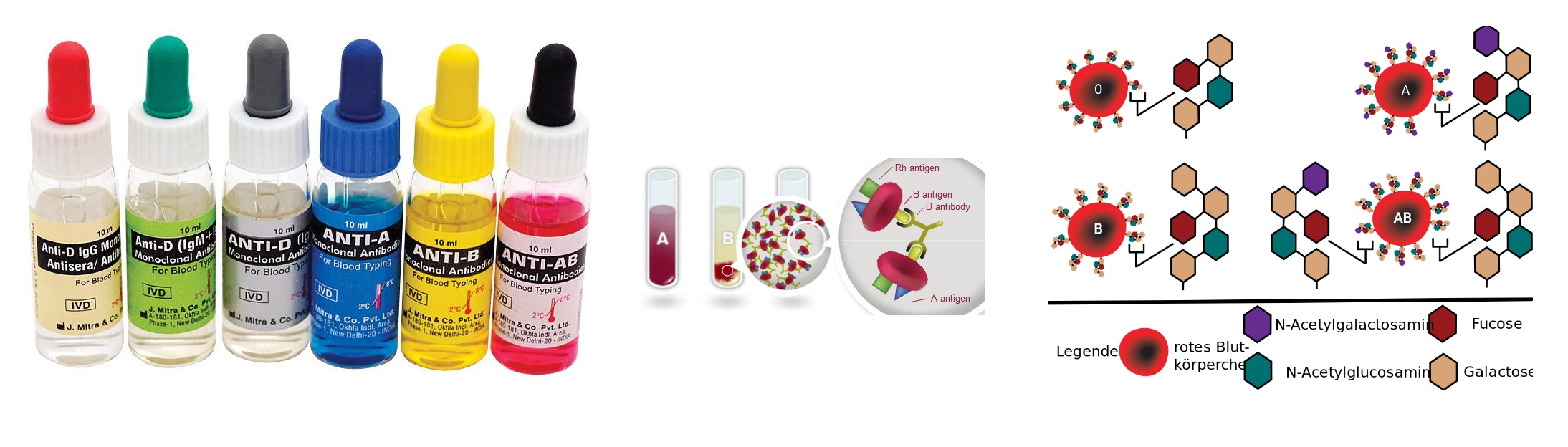
Reagents :
- Anti-A sera (Blue Colour; Contain Methelyne Blue)
- Anti-B Sera (Yellow Colour; Contain Riboflavin)
- Normal Saline (0.85% Sodium Chloride Solution)
Specimen :
10% suspension of Red Blood Cell in normal saline.
Preparation of Specimen :
- Mixed 5 drops of sedimented RBCs with 2 ml of normal saline ( 1 standard drop = 0.05 ml).
- Centrifuged at 1500 RPM for 1 to 2 minutes. Discarded supernatant by using a Pasteur pipette.
- Added 2 ml of normal saline to the sedimented RBCs and centrifuge at 1500 RPM for 1 to 2 minutes. (two times)
- Added 2 ml of normal saline to the sedimented red blood cells. Mixed well. These give a 10 % suspension of red blood cells (approx.).
Procedure :
- All the reagents ad sample to be brought to the room temperature before performing the test.
- Taken a clean and dry glass slide and make ‘A’ on the one edge of the slide and ‘B’ on the other edge of the slide and one line is marked on the middle of the slide by a marker pen.
- Placed 1 drop of Anti-A on the ‘A’ marked Side and 1 drop of Anti-B on the ‘B’ marked side of the glass slide.
- Added 1 drop of well mixed 10% red blood cells suspension to each half of the slide by using a Pasteur pipette.
- Mixed each sera with Cell suspension by using separate applicator sticks.
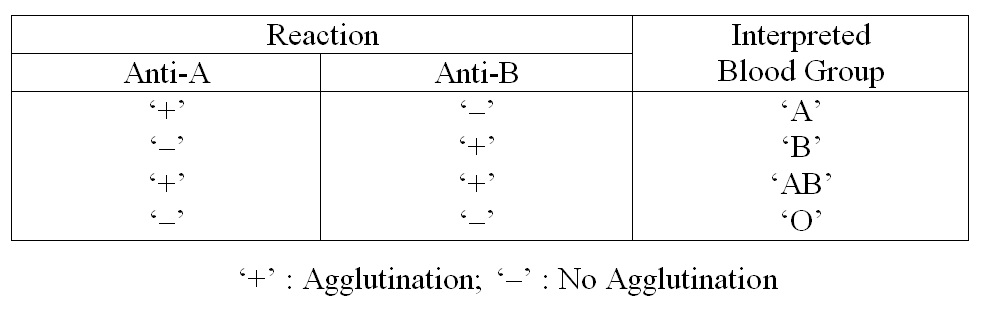
- Tilt the slide back and forth for 2 minutes and observe for agglutination by macroscopically (microscopically if required)
Interpretation :
Determination of ‘ABO’ Blood Grouping by Reverse Grouping
Determination of blood group by reacting known antigen (present on the surface membrane of the red blood cells) with unknown antibody (present in the serum). It also called Serum Grouping or Indirect Grouping.
Principle :
The procedures used with A-Cell and B-Cell are based on the principle of agglutination. Normal human serum contain antibody with clump in the presence of corresponding antigen.
Method :
Three methods are used for determination of ‘ABO’ blood grouping by Forward Grouping technique. These are as follows :
- Slide method
- Tube method
- Gel method
In the developing country Slide method is commonly performed. But Special circumstances Tube method as well as Gel method is performed. In the Laboratory We performed Slide method.
Requirements :
- Clean and dry grass free glass slide.
- Pasteur pipette.
- Applicator sticks.
- Centrifuge machine.
- Timer & Marker pen
- Microscope
Reagents :
- Pooled A-Cell (10% Red Blood Cell suspension with Normal saline).
- Pooled B-Cell (10% Red Blood Cell suspension with Normal saline)
Specimen :
Fresh Serum
Procedure :
- The entire reagents ad sample to be brought to the room temperature before performing the test.
- Taken a clean and dry glass slide and make ‘A’ on the one edge of the slide and ‘B’ on the other edge of the slide and one line is marked on the middle of the slide by a marker pen.
- Placed 1 drop of well mixed Pooled A-Cell on the ‘A’ marked side of the slide by using a Pasteur pipette.
- Washed the pipette with normal saline for 3 to 4 times.
- Placed 1 drop of well mixed Pooled B-Cell on the ‘B’ marked side of the slide by using Pasteur pipette. And wash the pipette 3 to 4 times with normal saline.
- Added 2 drops of clear fresh serum on the each cell suspension by using a Pasteur pipette. And wash the pipette 3 to 4 times with normal saline.
- Mixed the Serum & Cell suspension by using the separate applicator sticks.
- Tilt the slide back and forth for 2 minutes and observe for agglutination by macroscopically (microscopically if required).
Interpretation :




I’m definitely enjoying the information.