Blood Group and Pregnancy
‘ABO’ Blood Grouping & Pregnancy :
If Group-A blood is given (in error) to a group-B, a foreign substance (A antigen) is introduced into the blood stream of an individual who already has natural antibody (anti-A), which will reacts with the antigen on the incoming blood cells and cause them to agglutinate. This leads to serious problems such as blocking of blood vessels
as the incoming blood cells are agglutinated. This is forward by haemolysis of these cells as complement links to the antigen-antibody reaction.
The large number of incoming antigenic cells started an immune reaction leading to the production of Immune Antibody. These antibodies are IgG in nature. Which readily pass through the placenta and may therefore leads to mother-foetus ‘ABO’ incompatibility problem. This is particularly serious if the mother is ‘O’ type and the foetus type ‘A’, ‘B’ or ‘AB’. Immunization also occurs due to Foetal-maternal Haemorrhage when anti-A or anti-B antibodies are developed in mother by stimulation with foetal cells.
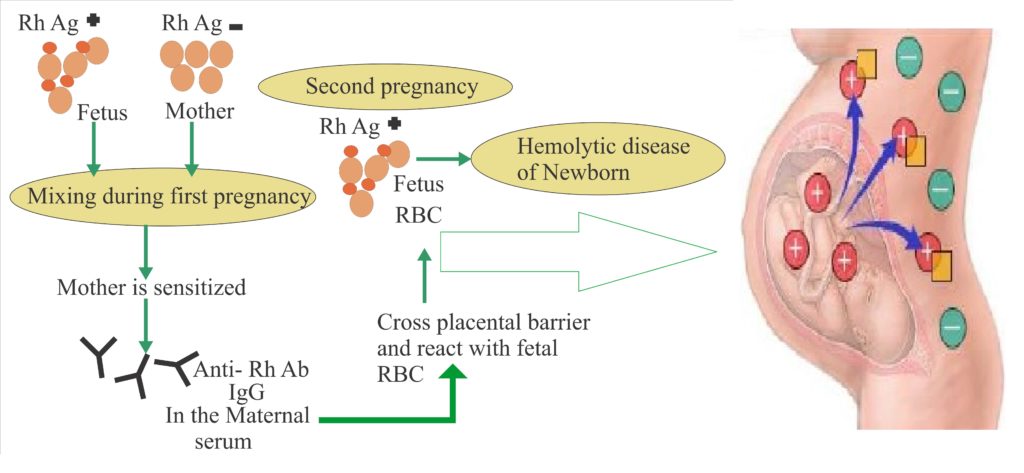 ‘Rh’ Typing & Pregnancy :
‘Rh’ Typing & Pregnancy :
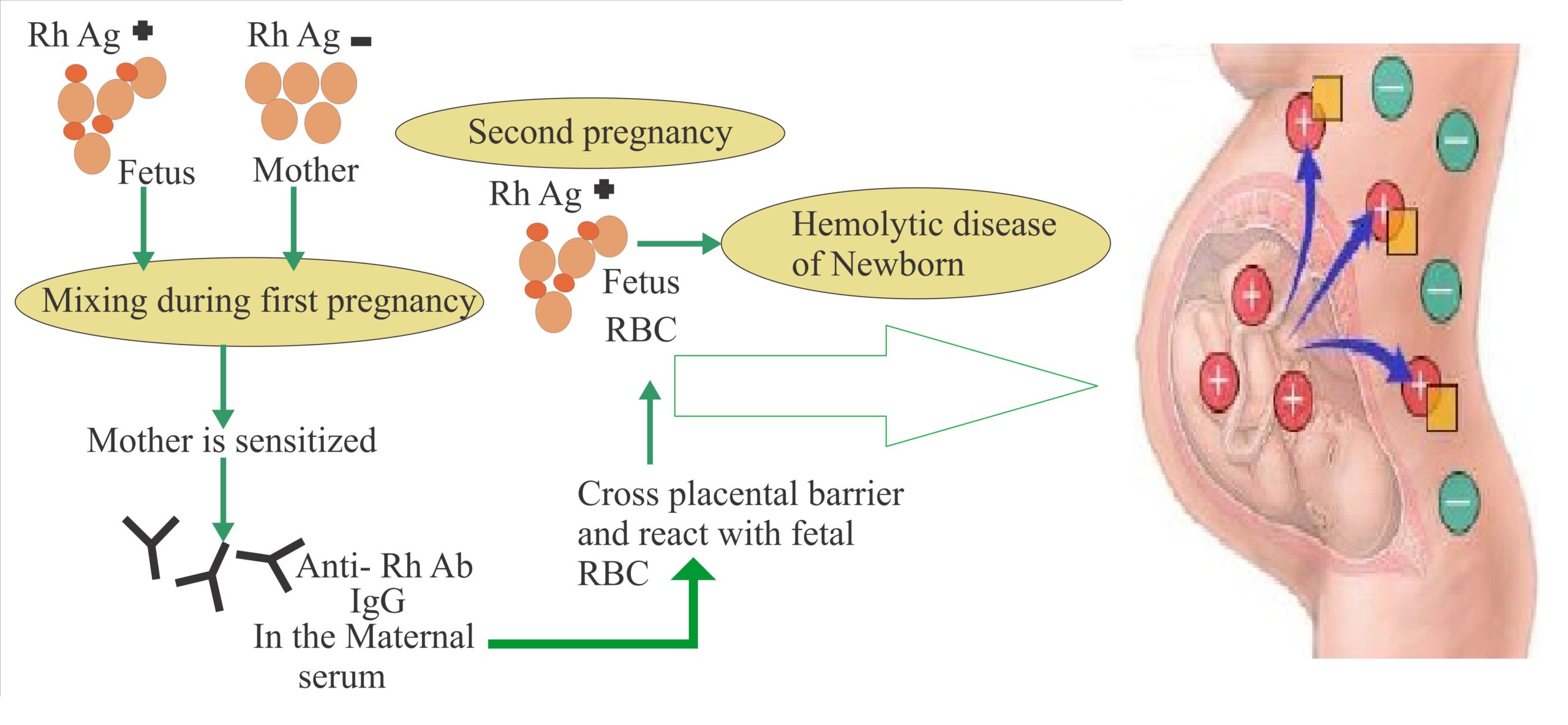
‘Rh’ factor have considerable significance in certain pregnancies. If a woman possesses ‘Rh’ Negative blood and her husband is ‘Rh’ Positive, there is strong possibility that the foetus will inherit the father’s dominant ‘Rh’ Positive factor. The foetus ‘Rh’ Positive cells produce antibodies in mother blood (in first pregnancy). These antibodies are IgG in nature and can pass through the placental barrier. Most ‘Rh’ problem arise during the second and third pregnancy, when antibodies form the stimulation of the first foetus pass through the placental barrier and destroy the cells in the developing foetus. If antibody titre is very high, the foetus may be die and be expelled before the end of normal gestation period. If the titre is low, the children may be born alive and develop Haemolytic Jaundice (Erythroblastosis foetalis). This may cause O2 starvation due to the destruction of oxygen carrying red blood cells.
In severe cases the child may die unless a complete replacement of blood is undertake immediately after birth, by Exchange Transfusion Technique.
Haemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN)
Haemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN) is an acquired haemolytic anaemia of the newborn characterized by a severe anaemia with erythroid hyperplasia, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly and hyperbilirubinemia. It has various clinical degrees, based on the severity of the symptoms. Some time it can be sever enough to result in intra-uterine
death, with the subsequent delivery of macerated foetus (hydrops foetalis).
Clinical jaundice may be absent for 24 hours after birth and thereafter deep unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia leading to Kernicterus (when serum Bilirubin enter the brain through crossing blood brain barrier) occurs. Sever cases shows cardiac failure and hydrops foetalis.
Clinical features of Haemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN) include anaemia, jaundice, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly and after Kernicterus.
In HDN, The mother is ‘Rh’ Negative while father and foetus are ‘Rh’ Positive. When the significant number of foetal cells enter into the mother blood circulation which may occur during placental separation at the time of delivery or abortion. This induces antibody response in the mother. The first pregnancy usually escapes provided the woman has not been previously sensitized by transfusion with ‘Rh’ positive blood. During subsequent pregnancy, the maternal anti-Rh antibodies (IgG in nature) cross the placenta and damage the foetal cells, producing Haemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN).
Laboratory Diagnosis of HDN:
Laboratory findings as birth :
- Cord blood :
- Variable anaemia (Haemoglobin <18 gm/dl).
- Reticulocytosis.
- Hyper-Bilirubinemia.
- Positive Direct Coomb’s test.
- Baby is ‘Rh’ Positive.
- Mother blood :
- Mother is ‘Rh’ Negative.
- Indirect Coomb’s test Positive with high plasma titre of anti-D.
Treatment :
If the Haemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN) is detected in intrauterine period, then Intrauterine Exchange Transfusion done (in special circumstances where serum Bilirubin level above the bulge of the Lilac’s chart). Exchange Transfusion is essential if HDN is detected after birth.
Prevention :
Anti Anti-D antibody (Rolin – band name) is injected intramuscularly after first time pregnancy if the foetus has ‘Rh’ Positive.


Hi everyone ,Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on sites I stumble upon everyday. Thanks
Very interesting information! Perfect, just what I was searching for! Thanks