Triglycerides (TG) – Significance, Characteristics, Function & Laboratory Analysis
Triglycerides (TG) or Triacyl glycerols are true natural fats, esters of trihydric alcohol, glycerol and fatty acids, that belong to the organic group of compounds called lipids. Most animal and vegetable fats are triglycerides. After hydrolysis they yield glycerol and fatty acids and the triglyceride assay is based on the quentitative analysis of glycerol forms of the tiglyceride. The triacylglycerols are the storage form of lipids in the adipose tissue. when stored as trihydric alcohol, water molecules are repelled and space requirement is minimal. Excess fat in the body leads to obesity. Triglycerides combine with protein in your blood to form substances called high-density and low-density lipoproteins. The lipoproteins contain cholesterol, which is one of the fats in blood that is related to heart disease.
As per international Union of Biochemistry the correct designations are monoacyl glycerol, diacyl glycerol and triacyl glycerol. But the old terminology of monoglyceride, diglyceride and triglyceride are still popular, especially among clinical laboratory worker.
- Naturally occurring fats and oils are mixtures of triglycerides.
- If all the three hydroxyl groups of the glycerol are esterrified to the same fatty acid, a simple triacyl glycerol is formed, e.g. Tripalmitin, Triolein, etc.
- A mixed triglyceride is formed, when different fatty acids are esterified to the hydroxyl groups of glycerol.
- Generally two hydroxyl groups are esterified to similar fatty acid the third with a different one, e.g. 1,3-dipalmitoy 1-2-olein; 1-palmitoy1-2,3-distearin, etc. When a PUFA is present, it is commonly esterified to the 2nd or β carbon atom.
They are hydrophobic and insoluble in water. Oils are liquids at 20°C ; they are triglycerides which contain a higher proportion of unsaturated fatty acids or short chain triglycerides. Oils are generally of plant origin. Fats are solids at room temperature and contain mainly saturated long chain fatty acids. Fats are mainly of animal origin. When the constituent fatty acids have a higher chain length in this condition these are predominantly saturated; ‘hard fat’ is formed (pig fat) and when Fats containing medium chain triglycerides or unsaturated fatty acids then these are soft fats (butter, coconut oil). Coconut oil contains mainly medium chain trihydric alcohol (Lauric and Myristic acids).
Hydrolysis of TG occurs in the body during digestion of dietary fat and mobilisation of triacyl glycerols from adipose tissue. Triglycerides in the body are hydrolysed by enzymes, lipases which are hydrolases. Triacyl glycerol is sequentially hydrolysed to diacyl glycerol and mono acylglycerol and finally glycerol plus 3 fatty acids. When triglycerides are hydrolysed by alkali, the process is known as saponification. The products are glycerol and soaps. Saponification number is defined as the number of milligrams of postassium hydroxide required to saponify one gram of fat. It is an incidication of the fat, and is inversely proportional to it. Human fat has a saponification number of 194-198, butter has 210-230 and coconut oil has 253-262.
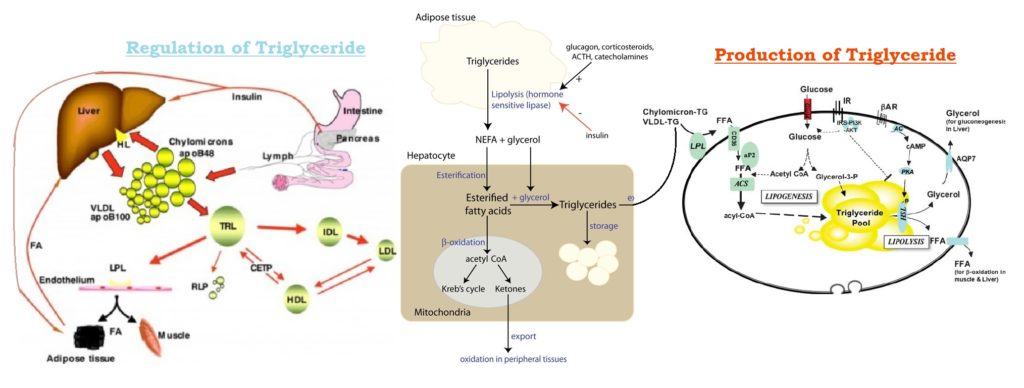
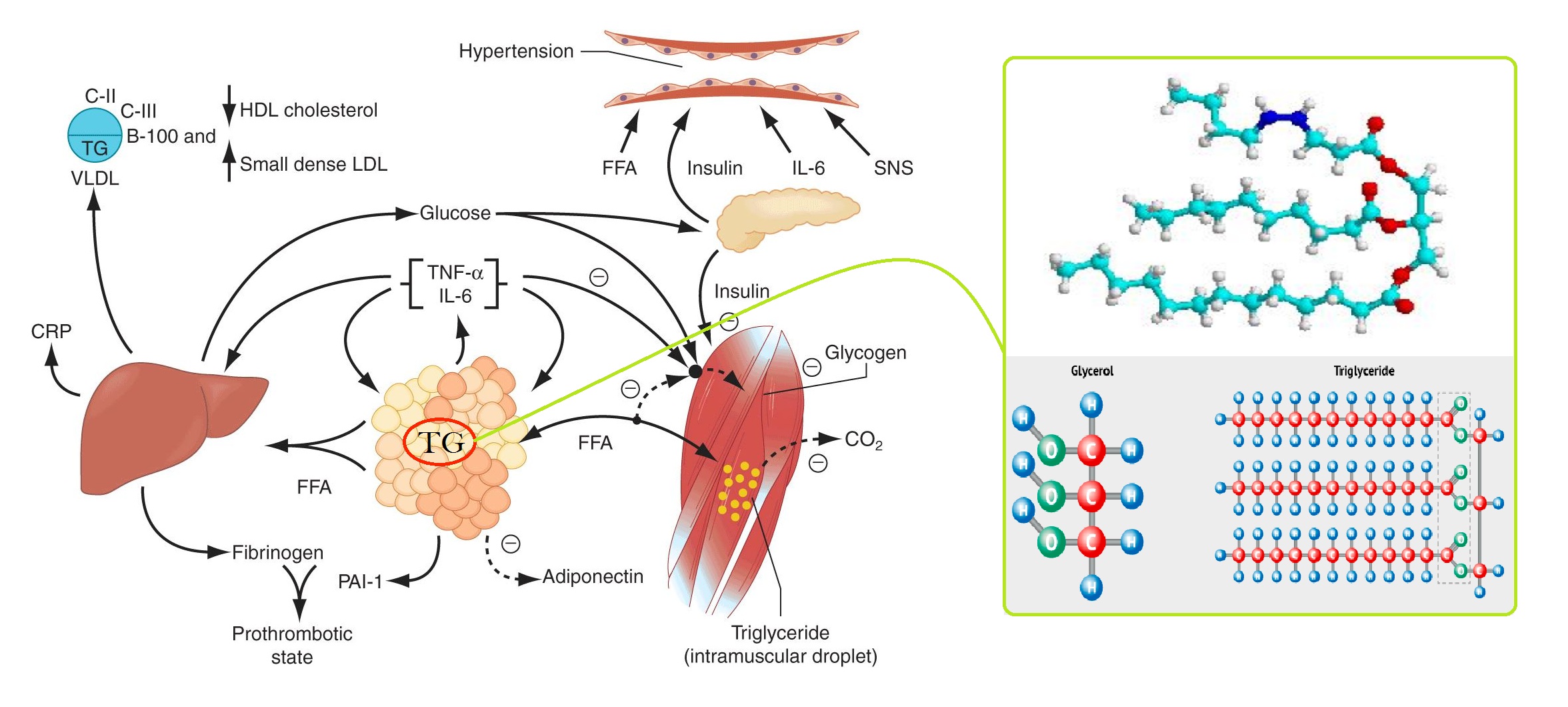
Triglycerides (TG) – Production & Regulation : https://medicoinfo.org/triglycerides-tg-significance-characteristics-function-laboratory-analysis/
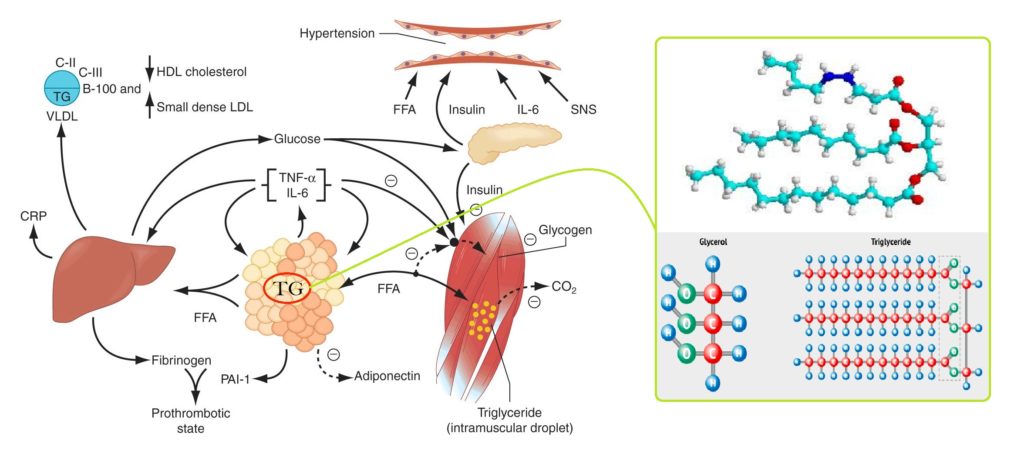
Elevated levels of triglycerides is serum have been identified as risk factors related to atherosclerotic disease that causes thickening of the walls of larger arteries. This may lead to a heart attack. some of the clinical conditions which cause hyperlipaemia are glycogen storage disease, nephrotic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases, some medications (birth control pills, steroids, & diuretics water pills etc.), chronic hepatitis and alcoholism.
The
most common reason someone might be advised to have their triglyceride levels
checked is to help assess their risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Most
common risk factors for Triglyceride level determination are smoking tobacco,
being overweight or obese, eating an unhealthy diet, such as high in saturated
fats, sugar, and alcohol & low in fruits and vegetables, being physically
inactive, having hypertensive person, history of severely high cholesterol or
premature heart disease, pre-existing heart disease and diabetes mellitus etc.
Triglyceride level check may also be ordered to monitor the success of
lipid-lowering lifestyle changes, such as improving diet and increasing
exercise, or for checking the effectiveness of drugs, such as fibrates,
omega-3s, niacin or statins etc. Some recommendation for healthy lifestyle
choices to decrease risk of heart disease and lower cholesterol and lower
triglycerides level are don’t smoking, daily physical activity, limiting saturated
fats diet, Eat less sugar and sugar-containing foods and drinks like soda.,
limiting alcohol drinking, maintaining a healthy weight, increasing fruits and
vegetables in daily life, choosing lean proteins, such as soy, fish, nuts,
beans and chicken etc.
LABORATORY ANALYSIS OF TRIGLYCERIDE MEASUREMENT
Triglycerides are family of lipid produced endogenously from carbohydrates and absorbed from the diet and are found in all plasma lipoproteins. Triglyceride measurement is an important tool in the diagnosis of hyperlipidemia. Increased concentration is found in hypertriglyceridemia, Ischemic heart disease, hypolipoproteinemia, nephritic syndrome, hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, acute pancreatitis, glycogen storage disease, and tangier disease etc. Decreased concentration is found in rare disease like Abetalipoproteinemia.
Normal Value:
- Normal : <150 mg/dl
- Borderline high : 150-199 mg/dl.
Method :
Enzymatic method (Three methods are ecommended for the determination of triglyceride level – Colorimetic method, Enzymatic method and Fluormetric method. Both the enzymatic and fluorometric methods require special equipment like ultraviolet spectrophotometer or fluorometer).
Principle :
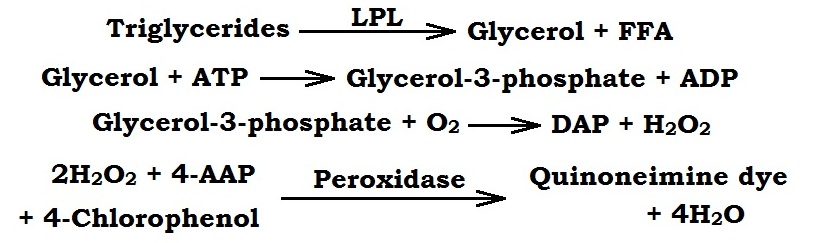
Triglyceride are hydrolyzed by lipoprotein lipase to produce glycerol and free fatty acid (FFA). In presence of glycerol kinase, Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) phophorylate Glycerol to produce Glycerol-3-Phosphate and Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP). Glycerol-3-Posphate is further oxidized by Glycerol-3-Phosphate Oxidase to produce Dihydroxy Acetone Phosphate and H2O2. In presence of peroxidase Hydrogen peroxidase couple with 4-Aminoantipyrine (4-AAP) and 4- Chlorophenol to produce red quinoneimine dye. The intensity of the produced colour is directly proportional to the concentration of triglyceride present in the specimen and which is measured by the photometer at 505 nm (500-530 nm, green filter).
Specimen:
Serum specimen is preferred, plasma can also be used for determining triglycerides. Anticoagulants such as EDTA should be used in case of the enzymatic method. For the colorimetric method, fluoride-oxalate can be used. Fasting samples are recommended for this analysis. Hence blood is collected before breakfast. The analysis should be done on the same day or the sample should be stored in the refrigerator for not more than 2 to 3 days. Haemoglobin and bilirubin in high concentration may interfere with the triglyceride analysis. Avoid a haemolysed serum specimen. A trace of detergent interferes with the test methodology, hence the glassware must be rinsed thoroughly with deionized water. Gross contamination of the specimen at any stage makes them unsuitable for true value of determination. The specimen should be brought to room temperature prior to the test.
Requirements :
- Reagents:
- GPO/
PAP enzyme reagent :
- 4-chlorophenol
- Glycerol Kinase
- Detergent
- Preservative
- Stabilizer
- Tri-glyceride standard : 200 mg/dl
- GPO/
PAP enzyme reagent :
- Test tubes and racks
- Pasteur Pipettes
- Distend graduated pipette
- Micropipette with tips
- Tissue paper
- Timer
- Colorimeter machine
- Incubator machine.
Procedure :
- All the reagents are brought to the room temperature before the test.
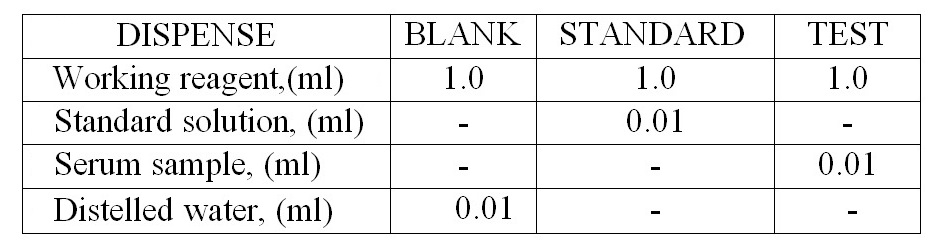
- Three dry and clean test tubes are taken and marked as Blank (B), Standard (S) & Test (T).
- Dispense the Working reagent, Triglyceride Standard, Distilled water & Serum in the above mention test tube respectively.
- Then mixed well.
- Incubated at 37°C for 10 minutes or room temperature for 30 minutes.
- The absorbance of the Test and Standard are measured against Blank in the colorimeter at 510 nm (500-530 nm, green filter).
- Standard concentration may be selected as per the absorbance of the test in case of higher absorbance of the test in case of higher absorbance higher concentration is taken.
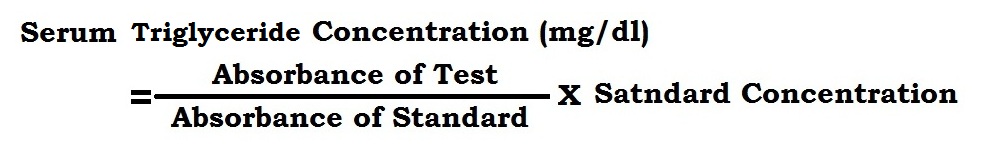
- Calculations :


Thanks for sharing your info. I really appreciate your efforts and I am waiting for your next write ups thank you once again.
Useful information. Fortunate me I discovered your web site by accident, and I am surprised why this twist of fate did not happened in advance! I bookmarked it.
I like what such intelligent work! Carry on the superb works guys…
I am extremely impressed with your writing skills as well as with the layout on your blog. Excellent quality writing, it’s rare to see a great blog like this one these days..
I’m really impressed with your writing skills and
also with the structure on your blog. Anyway stay up the excellent high quality writing,
it is uncommon to look a nice blog like this one nowadays..
I’m extremely impressed with your writing skills as well as with the layout on your weblog. Anyway keep up the nice quality writing, it’s rare to see a nice blog like this one now a days….
I found this article very interesting and good for me, it has a lot of info I need to know, thanks for sharing this helpful info…
Hi there! I’m at work surfing around your blog from my new iphone 4!
Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward
to all your posts! Carry on the fantastic work!