Quantification of Reticulocyte
Reticulocytes are juvenile red cells that pass into the blood stream from the bone marrow. Reticulocytes stay in the circulation for about 24 hours and matured into erythrocytes. Reticulocytes have ribosomal and cytoplasmic remnants which pick up supravital stains when the stain allowed penetrating the cells while in the living condition. Following this process of supravital staining, a blood smear is made and the numbers of reticulocytes are counted against the numbers of red cell observed in the smear.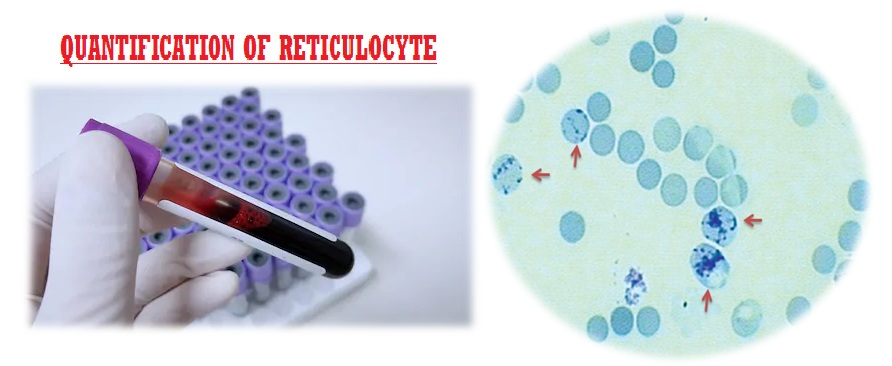
Clinical significance :
The number of reticulocytes in the blood circulation indicates the degree of activity of bone marrow. When the bone marrow is very active (in haemolytic anaemia or in acute blood loss) their number increased, this is known as reticulocytosis. In case of aplastic anaemia (poor activity of bone marrow) the reticulocytes count is decreased, this is known as reticulocytopenia.
Conditions for reticulocytosis :
- Haemolytic anaemia
- Immune hemolytic anemia
- Primary RBC membrane defects
- Sickle cell diseases
- Enzyme defects
- Exposure to toxins
- Regenerative phase of anaemia (Following treatment)
- Pernicious anaemia.
- Acute blood loss etc.
- Pregnancy and Infants (Physiological conditions)
Condition for reticulocytopenia :
- Aplastic anaemia
- Iron deficiency anaemia
- Hypoplastic anaemia.
- Myelofibrosis.
- Radiation sickness.
- Cytotoxic drug therapy.
- Untreated Pernicious anemia
- Bone marrow tumor etc.
Normal Values :
- Adult and Children : 0.2 – 2.0 %
- Infants (full term) : 2.0 – 6.0 %
- Childrens upto 5 years= 0.2-5.0%
The total count of reticulocytes is 24,000 to 48,000 per cu.mm of whole blood in normal condition. It is suggested that a count below 30,000 often indicates depressed erythropioesis.
Principle :
Supravital staining method is used for reticulocyte count. Blood is mixed with the stain and the basic dye enters in the cell under living condition. The RNA in the cell is precipitated by staining as dark blue network or reticulum. Blood smear is made afterwards. Since a direct count is not possible, a relative count is taken against the number of red blood cells and expressed as a percentages of red blood cells.
Specimen :
EDTA anticoagulated blood is commonly used but other anticoagulants interfere. Capillary blood can also be used (heparinized).The examination is performed with in 2 to 3 hours after blood collection, older specimen shows artifacts.
Requirements :
- Brilliant Cresyl blue stain :
- Brilliant Cresyl blue : 1.0 gm
- Sodium citrate : 0.4 gm
- Sodium chloride solution : 100 ml
- Or New Methylene blue stain :
- New Methylene blue : 0.5 gm
- Sodium chloride : 0.7 gm
- Sodium oxalate : 0.13 gm
- Distilled water : 100 ml
- Small and large test tube with test tube rack.
- Microscopic glass slide.
- Pasteur pipette.
- Counter machine.
- Spot-watch.
- Microscope etc.
Procedure :
(By using the New Methylene blue stain)
- Taken a clean and dry test tube in a test tube rack.
- Placed 2drops of New Methylene blue stain in the test tube by using a Pasteur pipette.
- Added 2 drops of well mixed blood in the reagent by using a same type of Pasteur pipette.
- Mixed well, covered the test tube with a cork to prevent evaporation and incubate at 37°C temperature for 15 minutes.
- Mixed the mixture and placed 1 drop of mixture on a clean and dry grease free glass slide and prepared a thin smear by the help of a Spreader slide.
- Air dry the smear, observed the smear and count the number of reticulocytes in respect of RBC under oil immersion objective (100X) of the microscope. Examine at least 15 fields having 100 – 150 RBCs in each field.
- Calculation :




You’ve done an excellent job. It’s truly fine, Great work, keep up writing…
I found this web page as a best website for most up-to-date updates.