Dopamine : Dose, Action, side effects and Contra-indications
Dopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter used to treat Cardiogenic shock, Chronic refractory congestive cardiac failure, low doses in renal failure, dilated Cardiomyopathy, hemodynamic imbalances, poor perfusion of vital organs, low cardiac output and hypotension, Multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, Tourette syndrome and schizophrenia etc.
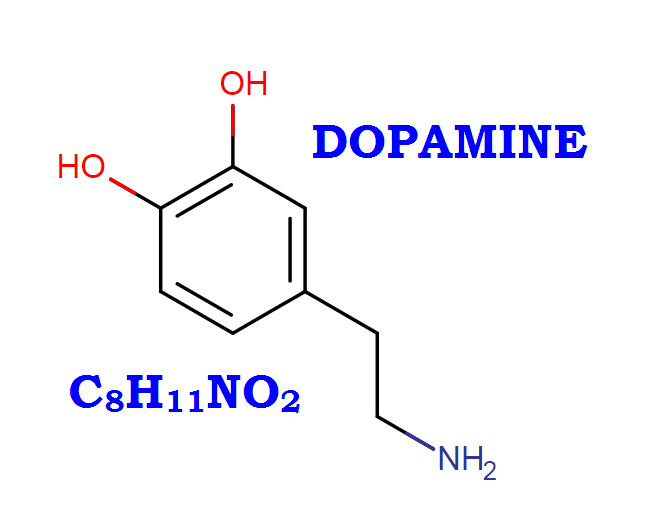
It’s one of the catecholamine neurotransmitters in the brain. It is derived from tyrosine and is the precursor to norepinephrine and epinephrine. Dopamine is a major transmitter in the extrapyramidal system of the brain, and important in regulating movement. A family of receptors (receptors, dopamine) mediate its action.
Dose of Dopamine Drugs
- Remal Dose : 5-20 μg/kg/min. Up to 4 μg/kg/min
- Inotropic dose with β action : 4-10 μg/kg/min
- α+β action : > 10 μg/kg/min
Action of Dopamine
- It is a direct beta-1 agonist which stimulates the heart and causes renal, mesenteric and cerebral vasodilation. Low doses increase renal blood flow, but large doses stimulate alpha receptors causing vasoconstriction and reduction of renal blood flow.
- Dopamine is a sympathomimetic agonist. It works on the receptors in the kidney, gut, brain and heart thereby relaxing the blood vessels in these organs. This restores the poor blood supply and oxygen delivery to these organs. It also causes an increase in urine production in the kidneys and protects them from injury.
Common side effects of Dopamine
- Flushing (sense of warmth in the face, ears, neck and trunk)
- Headache
- Increased heart rate
- Arrhythmia
- Angina, palpitations
- Nausea, vomiting
Contra-indications of Dopamine
- Pheochromocytoma
- VF/ V T